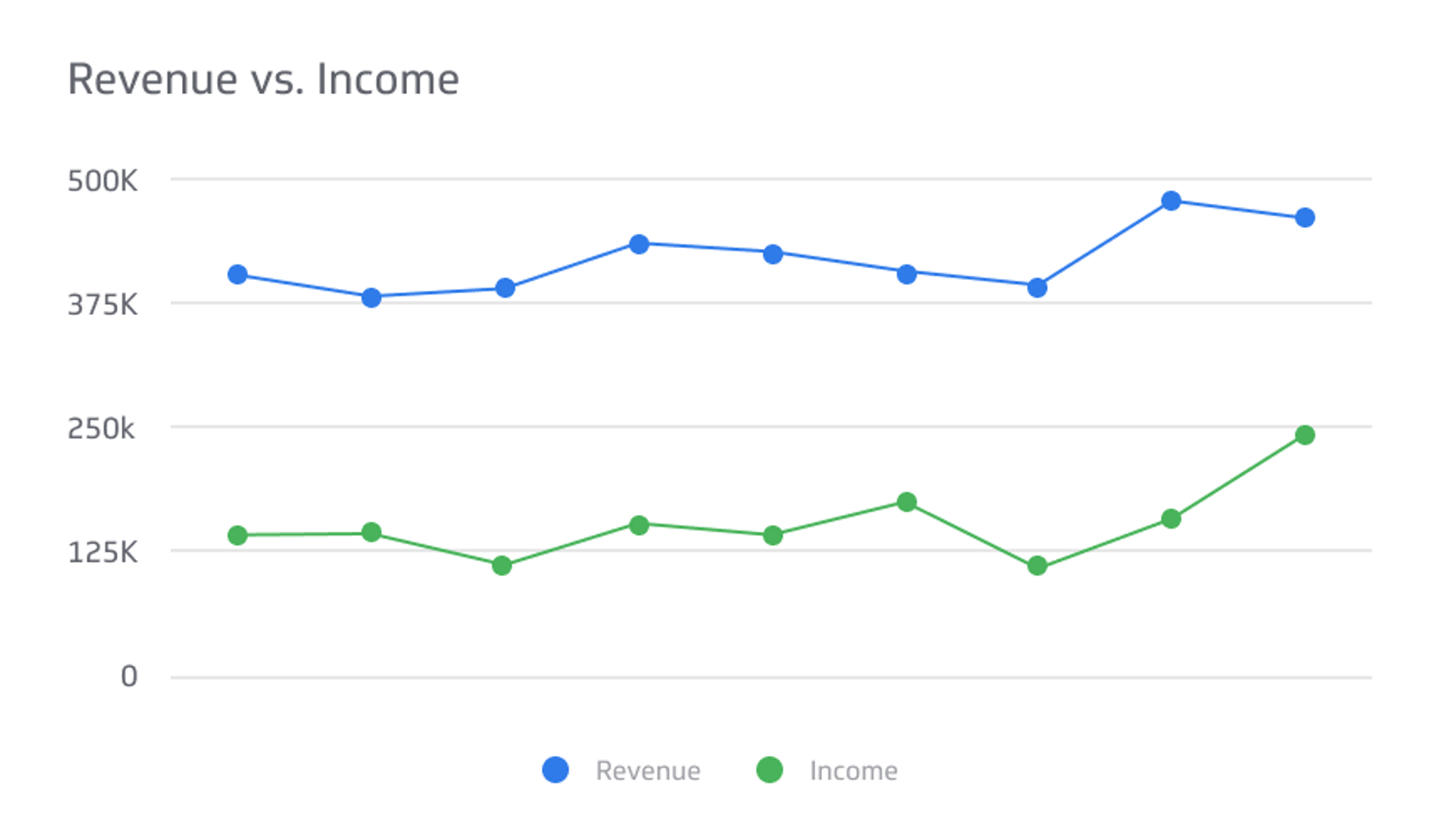
Revenue vs. Income
Revenue and income are two essential financial concepts that play a crucial role in determining the financial health of a business or individual.
Track all your Financial KPIs in one place
Sign up for free and start making decisions for your business with confidence.
As a business owner or marketer, you may have heard the terms "revenue" and "income" used interchangeably to refer to a company's financial performance. While there are some similarities between revenue and income, they aren't the same.
So how do revenue and income differ? Well, it's simple. The total amount of money a company earns from sales is revenue. While income is the money a company makes after accounting for expenses and other costs. Understanding the difference between revenue and income is essential to accurately assess a company's financial health and make informed business decisions.
In this article, we will explore the nuances between revenue and income and what it means for your marketing and business strategy.
What Is Revenue?
Revenue is a crucial financial metric that reflects a company's sales and growth potential. In accounting terms, revenue is recognized when a sale is made, regardless of whether payment is received. There are two main types of revenue: gross revenue and net revenue.
Gross revenue is the total amount of money a company earns from all its sales, without any deductions for expenses. Net revenue is the amount of revenue left after subtracting any discounts, refunds, returns, or additional costs directly associated with generating that revenue.
Different Types of Revenue
There are two main types of revenue: gross revenue and net revenue. Gross revenue is the total amount of money a company earns from all its sales, without any deductions for expenses.
Net revenue, on the other hand, is the amount of revenue left after subtracting any discounts, refunds, or returns, as well as any additional costs directly associated with generating that revenue.
Examples of Revenue
Examples of business revenue sources can vary depending on the industry and business model. In the retail sector, revenue is accrued from the sale of goods to customers, while in the service industry, revenue is generated from providing services to clients.
Businesses can earn revenue through licensing agreements, partnerships, or rental income. For example, a software company might earn revenue through licensing its software to other businesses, while a landlord might earn revenue through renting out a property.
It's essential to note that revenue does not necessarily reflect a company's profitability. High revenue does not necessarily mean high profit if the company also incurs high costs.
Therefore, businesses must analyze and understand the underlying costs associated with their revenue streams. Informed companies can make better decisions about their pricing strategies, operational efficiency, and overall financial health.
What Is Income?
The amount of money an individual or entity earns after deducting expenses and taxes is income. It refers to the amount of money an individual or entity earns after deducting expenses and taxes. It's a crucial financial metric that can provide insights into an individual's financial health and overall earning potential. In accounting terms, income is recognized when it is earned, regardless of when payment is received.
Different Types of Income
The two primary forms of income are gross income and net income. Gross income refers to the total money earned by an individual or entity before any deductions, while net income refers to the amount left after deducting expenses and taxes. Net income is also commonly referred to as profit or earnings.
Examples of Income
A salary is an income, and so are wages, tips, commissions, bonuses, and investments. We recommend having many streams of income, whether that is a job, an investment such as stocks, or rental properties.
Monitor your income over time. With this knowledge, you will make better decisions about spending habits, savings goals, and overall financial planning.
Remember that external factors such as economic conditions, tax laws, and industry trends can affect income. Companies should be aware of changes in their industry or market and adjust their income strategies accordingly.
By now, you understand that revenue means all the money a company receives from selling goods and services, whereas income is the revenue minus qualifying expenses. Here is more information to keep in mind:
Calculating Revenue vs. Income
Revenue and income represent different aspects of a company's finances. A detailed analysis of your company's revenue vs its income provides a more accurate picture of its profitability. So how do you know your company's revenue vs its income? Revenue is determined by multiplying the price of a product or service by the number of units sold. Income is calculated by subtracting all expenses and taxes from the total revenue.
A company with high revenue and high expenses won't be profitable. This is why companies must analyze their earnings.
Aside from the points mentioned earlier, revenue and income are significant for investors and stakeholders in a business. They use these metrics to evaluate a company's financial performance and make investment decisions.
In a company's income statement, revenue typically appears near the top. The net figure is near the bottom, also known as the "bottom line." As a result, revenue is a larger category that includes income as a subset.
Factors That Affect Revenue vs. Income
Various factors can affect the revenue and income of a business, some of which are beyond the company's control. Here are a few examples.
External Factors
The state of the economy, level of competition, and consumer behavior can significantly impact the revenue and income of a business. For instance, during a recession, consumers may reduce their spending, which leads to decreased revenue and income for businesses that rely on discretionary spending.
Similarly, a highly competitive market can force businesses to lower their prices to remain competitive, which can reduce revenue and income.
Internal Factors
Pricing strategy and operational efficiency are internal factors that can significantly impact revenue and income.
Businesses with a well-planned pricing strategy can attract customers and generate higher revenue. For example, premium pricing can help a business increase revenue and income by targeting customers willing to pay a premium for high-quality products or services.
Operational efficiency can have a significant effect on revenue and income. Lean manufacturing practices, or investment in technology, streamline business operations, reduce costs, and increase profitability.
Businesses must be aware of the external and internal factors that can affect their revenue and income. By doing so, they can optimize their revenue and income and minimize their risks.
Is Revenue More Important Than Income?
Although both metrics play a vital role, income is often considered more significant than revenue since it represents a business's profit.
It indicates the company's ability to cover all its expenses and further invest the profit into the business without relying on external funding like loans to keep it afloat.
While a company with robust revenues may show it can sell its product or service, a business with high profits is likely more financially sound.
Examples of Revenue vs. Income
Revenue and income are critical components in both business and personal finance.
Consider the following examples:
Real-World Examples
Here are real-world examples of how revenue vs. income looks:
- Apple Inc.: In 2020, Apple Inc. reported revenue of $274.5 billion from the sales of its products and services. However, the company's net income for the same year was $57.4 billion, a small fraction of its revenue. This shows that although Apple generated massive revenue, its net income was still a relatively small percentage of the total revenue.
- A small restaurant: A small restaurant may generate $500,000 in revenue per year from food sales, but after deducting expenses such as rent, labor costs, and supplies, the net income may be only $50,000. In this case, the revenue is relatively high compared to the net income, meaning the restaurant has significant expenses to cover before realizing a profit.
- An individual investor: An individual investor may earn revenue from dividends and interest payments on their investments, which may total $10,000 per year.
However, after deducting expenses such as brokerage fees and taxes, the net income may be only $7,000. This means that although the individual investor earned a significant amount of revenue, their net income was lower due to expenses.
Final Thoughts
Revenue and income are two essential financial concepts that play a crucial role in determining the financial health of a business or individual.
While revenue is the total earned from sales or other sources, income is the profit earned after accounting for all expenses.
Understanding the difference between revenue vs income is crucial for making informed financial decisions, such as budgeting, investing, and pricing strategies.
Businesses and individuals can improve their financial performance and make better choices by considering the factors that affect revenue and income. We recommend analyzing revenue and income statements regularly and seeking professional financial advice when necessary to ensure financial success.
Related Metrics & KPIs