Gross Churn Vs. Net Churn
Understanding the distinction between Gross Churn and Net Churn is crucial for businesses seeking to improve customer retention and achieve sustainable revenue growth.
Track all your Financial KPIs in one place
Sign up for free and start making decisions for your business with confidence.
In today's competitive business landscape, managing customer churn is essential for sustainable growth. But one aspect that often confuses businesses is the distinction between Gross Churn and Net Churn.
In this article, we'll explore the definitions, calculations, and significance of these metrics. Understanding these financial metrics allows you to develop targeted strategies to enhance customer retention and revenue expansion. So let's get started!
Definition Of Gross Churn And Its Calculation
Gross churn, or customer churn, is a vital metric that helps businesses track the revenue lost due to customer cancellations. It measures the percentage of customers who cancel or do not renew their subscriptions within a specific period.
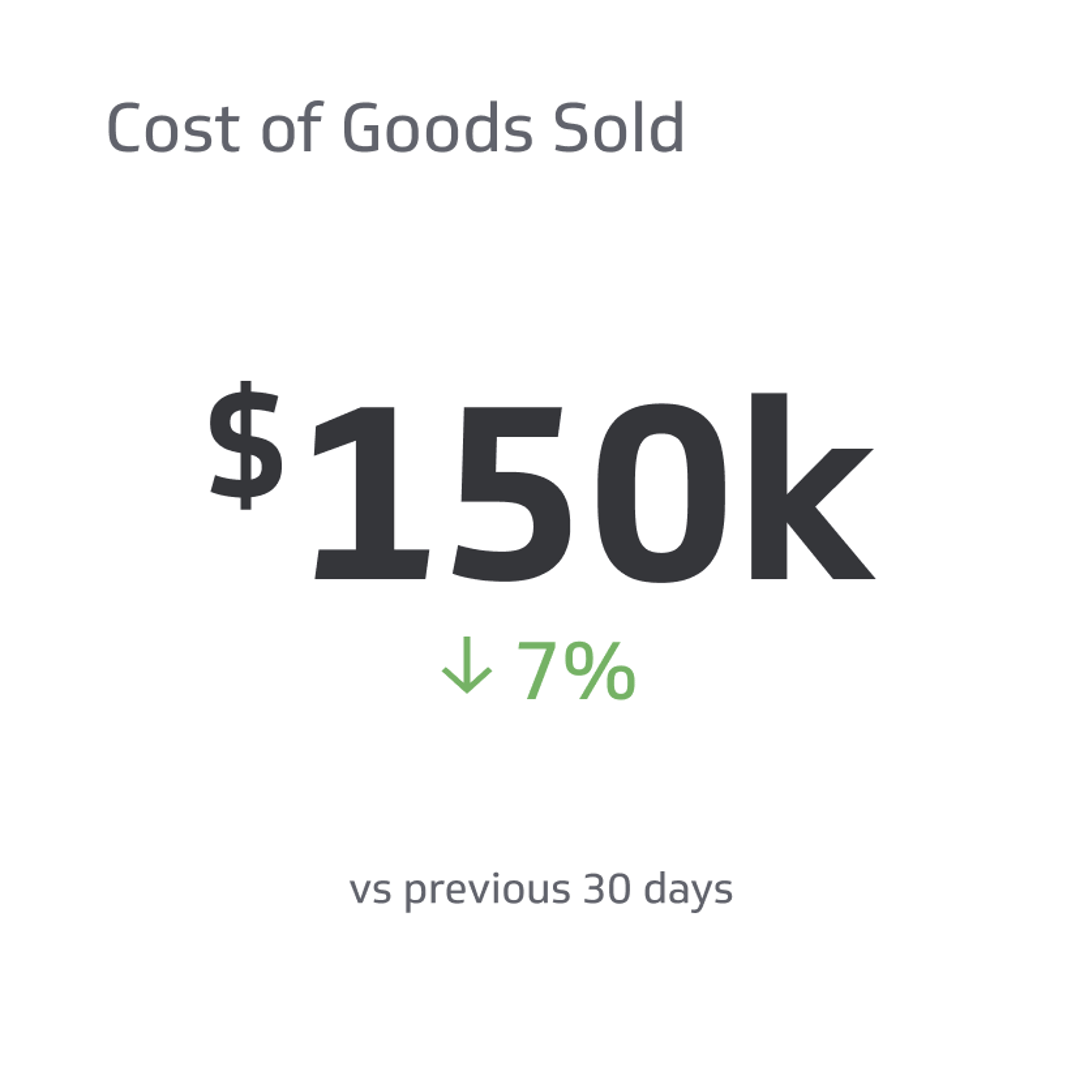
To calculate gross churn, divide the number of lost customers by the initial number of customers and multiply by 100. For example, if a music streaming service starts with 1,000 subscribers and loses 50 subscribers, the gross churn rate would be 5%.
Definition Of Net Churn And Its Calculation
Net Churn, also known as revenue churn or MRR (Monthly Recurring Revenue) churn rate, considers lost revenue from customer cancellations and gained revenue from existing customers through upsells, cross-sells, or subscription upgrades. It provides a view of the net impact on a company's recurring revenue.
To calculate net churn, subtract the revenue gained from existing customers from the revenue lost due to cancellations and downgrades. Then divide the result by the total revenue at the beginning of the period.
For example, if a business has three customers with monthly revenues of $20, $40, and $60 and experiences a cancellation of $20, a downgrade of $10, and gains $15 from an upgrade, the net churn would be -5%.
A negative net churn rate indicates that despite some losses, the company achieved overall growth in monthly recurring revenue thanks to existing customer expansion.
Key Differences Between The Two
Gross churn and net churn differ in their calculations and what they represent. Gross churn measures the revenue lost from canceled subscriptions divided by total monthly recurring revenue (MRR). It focuses solely on the revenue loss from customer attrition without considering gains from new customers or existing customer expansions.
On the other hand, net churn considers both losses and gains by calculating the MRR Churn Rate as a percentage and subtracting the expansion MRR percentage.For example, let's compare two music streaming services, MusicBoxProApp (MBP) and TuneCraveStream (TCS).
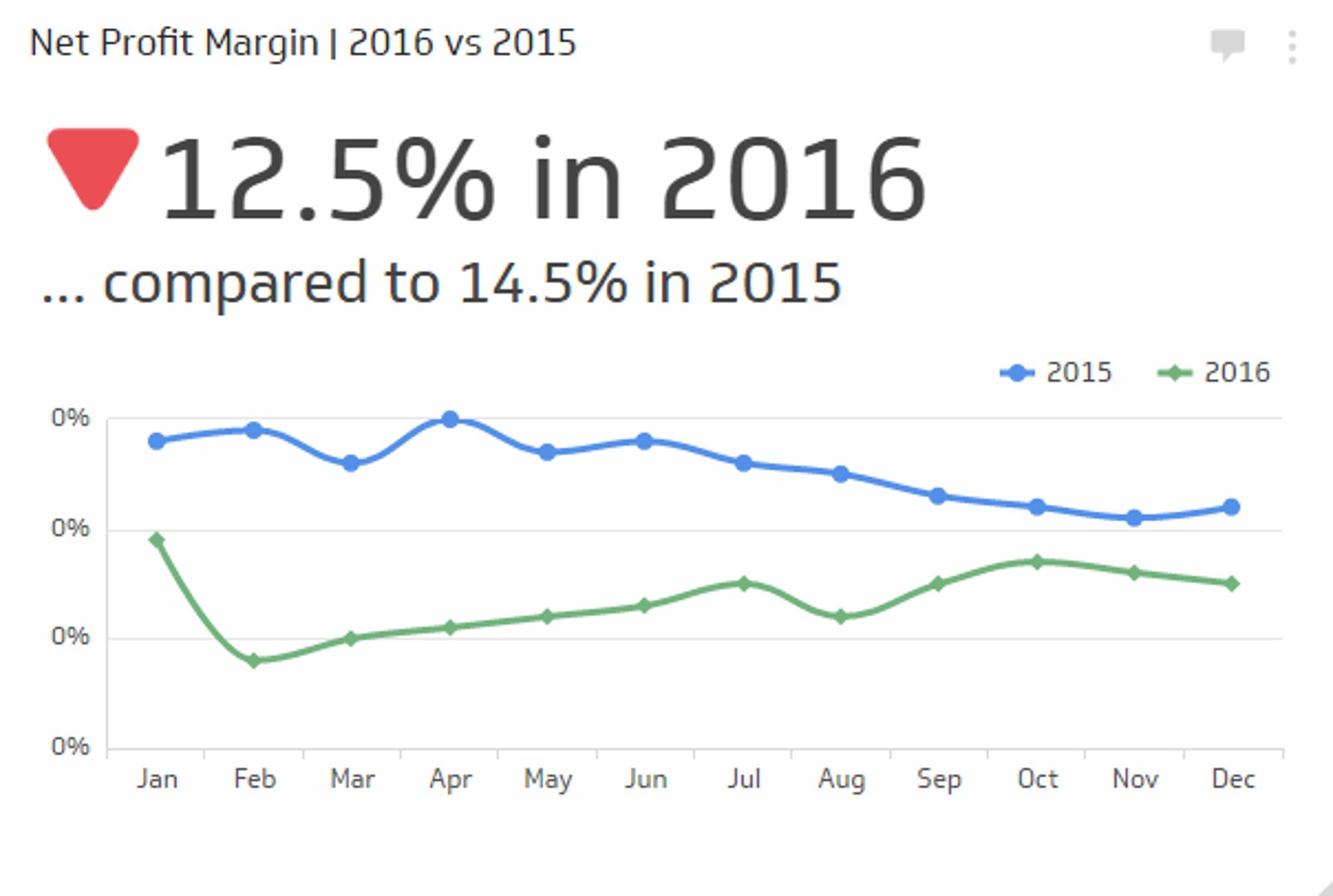
MBP has a gross churn rate of 8%, indicating it loses 8% of its MRR each month due to subscriber cancellations. TCS has a lower gross churn rate of 4%. However, when considering net churn rates, which include additional sales from loyal customers' recommendations or upgrades, MBP performs better with a negative net churn rate of -1%.
This means MBP recovers more than its original losses through improvements like upsell campaigns or plan upgrades among existing subscribers.
The Importance Of Calculating Gross And Net Churn Rates
Calculating gross and net churn rates is crucial for businesses as it offers valuable insights. Let's delve into their significance:
Indicators Of Customer Retention And Revenue Growth
Calculating gross and net churn rates is crucial for understanding customer retention and revenue growth. Monitoring these metrics provides insights into customer behavior and preferences, enabling businesses to improve or remove features contributing to high churn rates.
Insights Into Customer Behavior And Preferences
Calculating gross and net churn rates offers insights into customer behavior. Additional analysis of customer data like demographics, purchasing patterns, feedback, and online activity helps understand the drivers of churn and identify areas for service improvement.
Helps With Forecasting And Decision-making
Calculating gross and net churn rates is essential for businesses, particularly in subscription-based industries like music streaming services. A thorough understanding of churn enables informed decisions about marketing campaigns and product development.
By forecasting revenue losses and predicting gains from reducing churn, companies can make data-driven decisions, avoiding costly mistakes based on speculation.
Reducing Gross And Net Churn: Strategies For Success
Reducing churn rates is a top priority for businesses as it directly impacts customer retention and revenue growth. Let's explore how it achieves these outcomes:
Improving Customer Experience
Enhancing the customer experience is a highly effective strategy for reducing gross and net churn rates. Positive customer interactions increase the likelihood of customer retention. To achieve this, businesses should invest in delivering high-quality products, exceptional customer support, and personalized experiences tailored to individual needs.
Improvements can be made through resources like tutorial videos, prompt response times, loyalty programs, incentives, and feedback surveys to gather insights for continuous enhancements.
Personalized Solutions
Implementing personalized solutions is an effective approach to reducing both gross and net churn rates. Businesses can enhance customer retention by tailoring experiences to individual customer needs and preferences.
For instance, a music streaming service can offer personalized playlists based on users' listening history or recommend local concerts of their favorite artists. Personalization not only improves retention but also drives revenue through targeted upselling opportunities.
Offering Incentives And Rewards
Incentives and rewards for existing customers are powerful strategies to decrease gross and net churn rates. Businesses can implement loyalty programs with perks or discounts for continued service use and referral bonuses for customer acquisitions.
Spotify, for instance, provides premium subscribers with personalized playlists, music recommendations from experts, and discounted family plans. These incentives enhance customer retention, which differentiates the business from competitors.
Continuous Customer Engagement
Continuous customer engagement is vital in reducing both gross and net churn rates. Businesses like Netflix excel in this by leveraging personalized recommendations based on users' viewing activity.
By analyzing user preferences and behaviors, Netflix suggests relevant shows and movies tailored to individual tastes, keeping users engaged and satisfied. This level of personalization creates a unique experience that encourages subscribers to continue using the service, reducing churn and fostering long-term customer loyalty.
Importance Of Tracking Progress And Adjusting Strategies
Tracking progress and adapting strategies is crucial in reducing gross and net churn rates. Churn rates are dynamic and influenced by customer behavior, competition, and market trends.
Regular monitoring of churn rates and key SaaS metrics like Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR), Customer Lifetime Value (CLV), and Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) provides valuable insights for customer retention and revenue growth. This data helps businesses identify areas needing adjustments and optimize their approach to enhance performance.
Conclusion
To sum up, understanding the distinction between Gross Churn and Net Churn is crucial for businesses seeking to improve customer retention and achieve sustainable revenue growth. These metrics offer valuable insights into customer behavior, preferences, and satisfaction, enabling accurate performance forecasting.
It's essential to develop tailored strategies that address the unique challenges of different industries, as churn rates vary across sectors. Ongoing customer engagement through personalized solutions such as incentives, rewards programs, and improved experiences is critical to effectively reducing both types of churn.
Related Metrics & KPIs