Net Profit
Net profit is the total amount of money left after deducting all expenses.
Track all your Financial KPIs in one place
Sign up for free and start making decisions for your business with confidence.
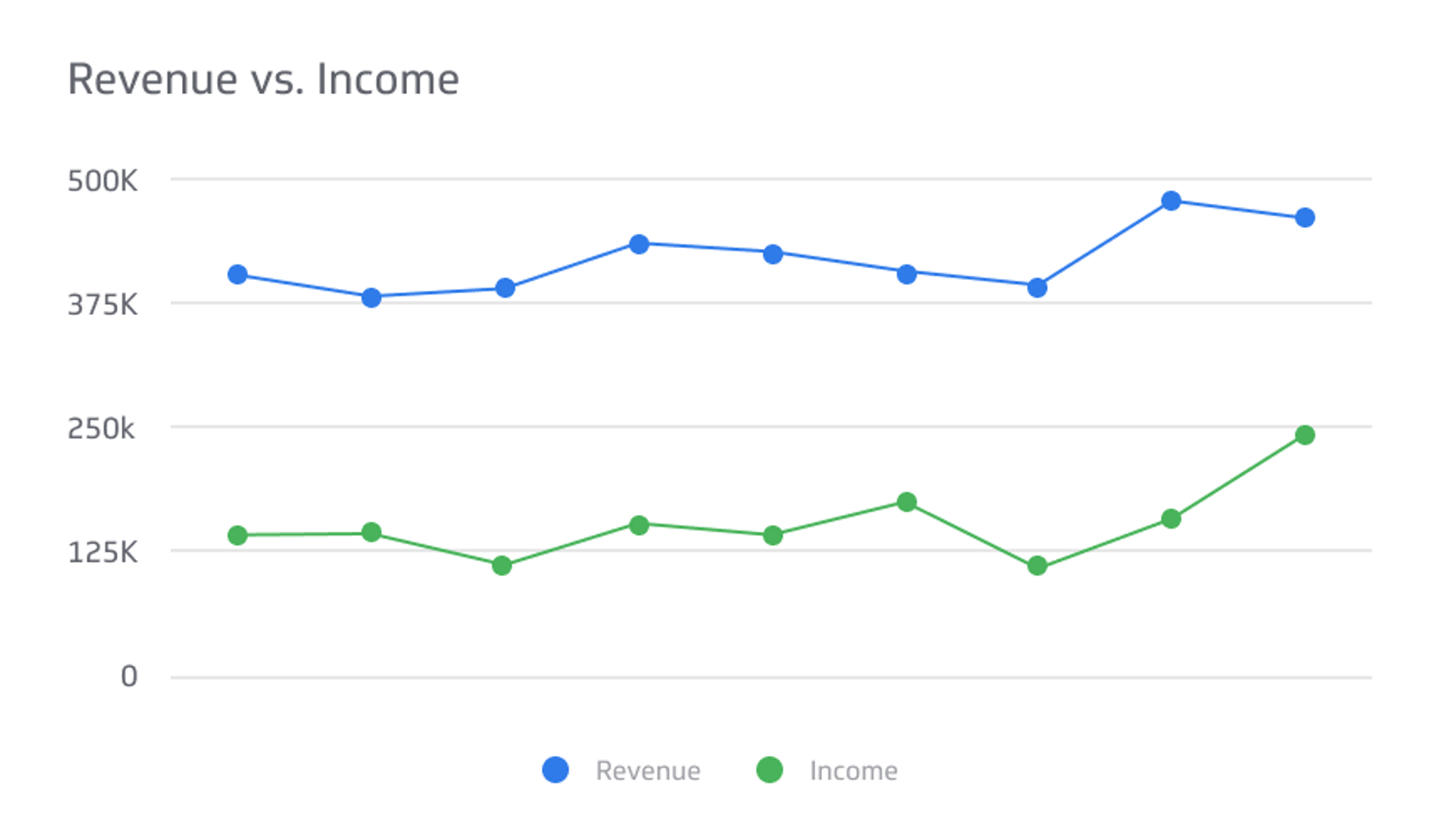
Net profit is one of the most critical metrics in business management and e-commerce analytics. In a nutshell, net profit is the total amount of money left after deducting all expenses. Often denoted as net income or net earnings, net profit is a crucial indicator for retail and e-commerce businesses since increased business revenue doesn't always indicate higher profitability.
Net profit represents the "bottom line" figure of what you made from your business endeavor. For the consistent growth of your business, you will need to maintain your company's net profit at the end of each quarter. Expanding your business allows you to use your net profit to begin new projects, pay off debts, and save for future expenses.
Why Is Net Profit an Important Metric?
Every successful firm has to have a clear plan for growth and expansion. A company may increase its business revenue but still be unprofitable. With a steady analysis of your firm's net profit, you can tell if projects are actually profitable and adjust your business strategies accordingly.
If your business' net profit indicates improving profitability, you can invest in expanding your business. You may prefer increasing your production or marketing budget, but it is important to keep evaluating your company's net profit to assess the viability of your ventures.
How to Calculate Net Profit
Net profit is a straightforward calculation. However, gathering all the information required for an accurate estimate is often a hassle. Net profit involves subtracting all your business expenses for a particular duration from your total revenue for the same period.
Hence the formula:
Net profit = Total Revenue – Total Expenses
Here is a simple example of net profit calculation for a soap-making company: The soap company earns $370,000 in revenue in a month, with operating expenses of $40,000 and the cost of goods sold at $30,000. Salaries were allocated $80,000, and taxes took up $5,000. To calculate the net profit for the company, you must add all the expenses (operating expenses + cost of goods sold + salaries + + taxes) and subtract the figure from the total revenue.
Total Expenses = $40,000 + $30,000 + $80,000 + $5,000 = $155,000
Net Profit = $370,000 – $155,000 = $215,000
It is important to note that while net profit is a measure of your profits in a given period, it may not capture most of your non-cash expenses, such as amortization and depreciation. Therefore, net profit cannot be taken as a measure of your earnings for a particular duration.
Which Expenses Affect Net Profit?
Two basic types of expenses must be factored into the calculation of your company's net profit for an accurate estimate: variable and fixed expenses. Variable expenses include the cost of goods sold and vary on the scale of production or sale.
These expenses are incurred during the product's procurement or creation. Variable expenses for production companies often include:
- Cost of raw materials
- Packaging
- Production technology
- Production wages
- Equipment depreciation
- Utilities for production space
Variable expenses are easier to calculate for e-commerce businesses since they are simply the cost of purchasing and shipping the products you are selling.
In contrast, fixed costs, or operating expenses, are unlikely to vary significantly from month to month. They include:
- Rent
- Taxes
- Wages for employees in other departments not involved in production
- Marketing expenses
- Employee benefits
- Business travel costs
- Research and development costs
- Administrative expenses
Fixed costs include all non-production costs, which also take into account other expenses incurred to cater for product marketing, delivery, promotion, and accounting.
Other Expenses
There are other expenses that you need to consider when determining your company's net profit. Non-operating expenses, such as losses from investments in other firms as well as proceeds from other ventures, are also included in the net profit calculation.
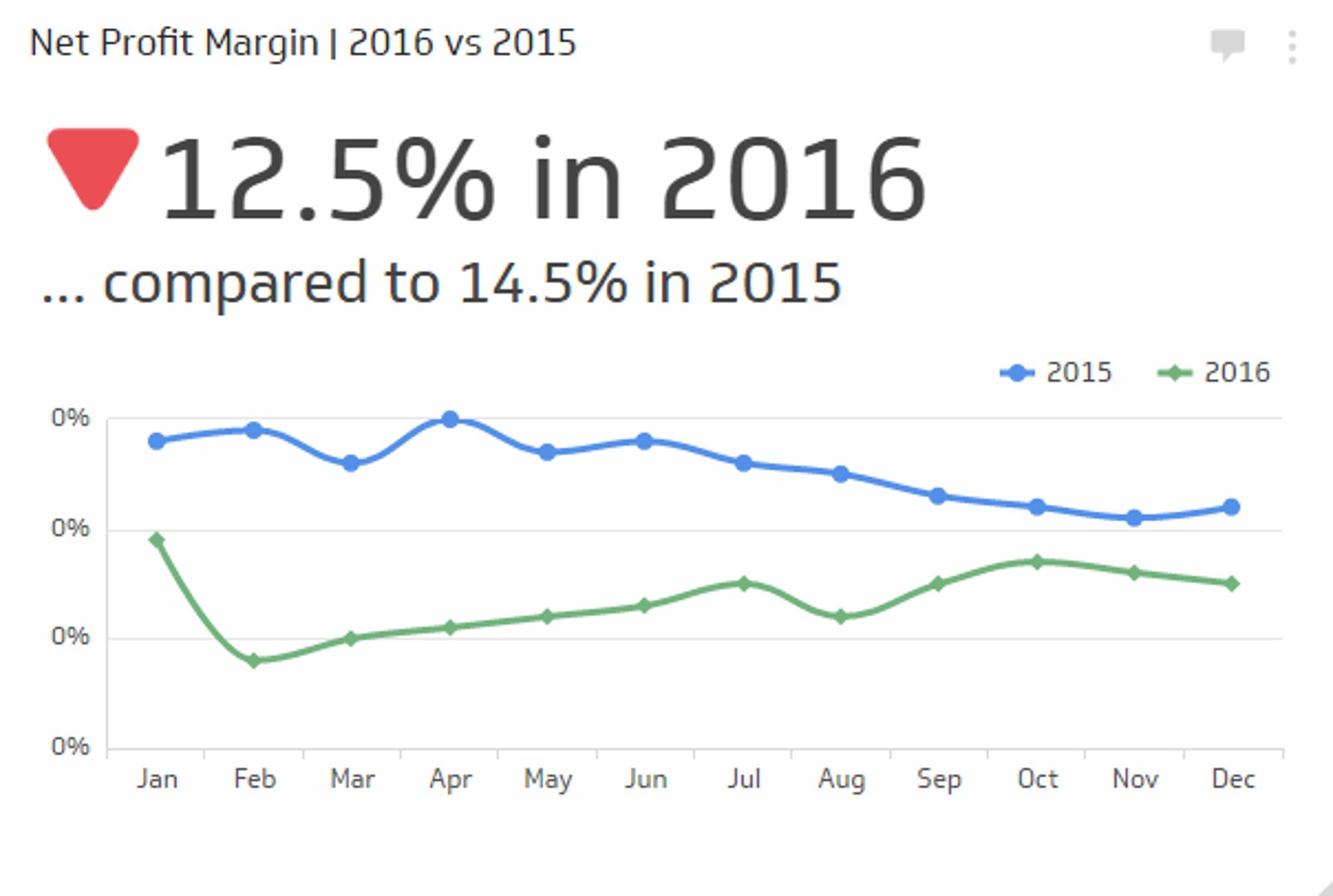
Calculating Net Profit Margin
Net profit margin depicts the ratio of the net profit of a business to its total revenue. It is simply the net profit as a percentage of total business revenue. To calculate the net profit margin of a firm, you need to divide the net profit by the total revenue and multiply the result by a hundred.
From the example used above, the net profit of the soap-making company was $215,000, and its total revenue was $370,000. Hence the net profit margin for the firm would be:
$215,000/$370,000 x 100 = 58%
The soap-making company has a net profit margin of 58%, which means the firm makes 58 cents in net profit for every dollar earned as revenue.
How to Increase Your Net Profit
Improving a company's net profit is a gradual but strategic process. There are various ways a company can improve its net profit, including:
Review Product Pricing
A price adjustment, however minimal, may be all you need to improve your net profit. Keeping the current market status in mind, optimize your product pricing and apply pricing strategies to retain your customers. It is, however, essential to carry out some market analysis to avoid setting prices that your customers are not willing to pay.
Get Rid of Unprofitable Products and Ventures
Some products or services may yield low profits, yet they take up a significant portion of your company's expenses. Removing such products and services clears up your shelf space for more profitable products and eliminates all costs related to their production and sale. You can quickly identify the products and services to remove by periodically reviewing your inventory for unprofitable ventures.
Reduce Variable Costs
You may be able to reduce your cost of goods sold, whether creating your own products or reselling items. For instance, as a retailer, you may be in a position to find a cheaper source for your items or negotiate a lower amount with your current supplier.
Manufacturers could apply a wider range of reductions in the production phase by either streamlining their production processes or seeking cost-efficient materials. These changes could go a long way in increasing a company's net profit.
Cut Back on Overhead Costs
Overhead costs consist of expenses incurred in running your business. Whether it is office supplies, travel expenses, or marketing costs, there is likely an expense that you could reduce to improve your net profit. Carry out a detailed review of your firm's overhead expenses and identify departments or processes that use up more costs and how you could reduce them.
You could also find restructuring your company an ideal option to cut back on the numerous overhead costs that you have identified. That way, you could also optimize various departments for higher productivity and further improve your company's net profit.
Takeaway
You can now calculate your net profit by deducting your business expenses from the total revenue. It is essential to calculate the net profit of your firm as it indicates the profit earned from a business venture in a given period. Continuous assessment of this crucial financial metric allows a business to optimize its processes and create a clear plan of expansion.
By better understanding the factors that affect net profit and how to calculate it accurately, you offer your business a better chance at growth.
If you want to have a better sense of your business status and how you could improve it, reach out to us or visit our website today. We understand that the growth and expansion of your business are anchored in your ability to understand its current needs and optimize its operations accordingly.
Related Metrics & KPIs