What is a KPI, Metric or Measure?
Published 2026-02-18
Summary - Discover the differences between KPIs vs metrics vs measures? How are they similar but different, and why?
Not sure about the differences between KPIs, metrics, and measures? You’re in the right place. By the end of this post you’ll know what each term means and why each one matters. You’ll also have practical, memorable examples. For more hands-on advice, check out the Metric Stack podcast.
Before diving into the terms and what sets them apart, it’s worth noting that many people use KPI and metric interchangeably in the dashboard and reporting space. Let’s clear that up.
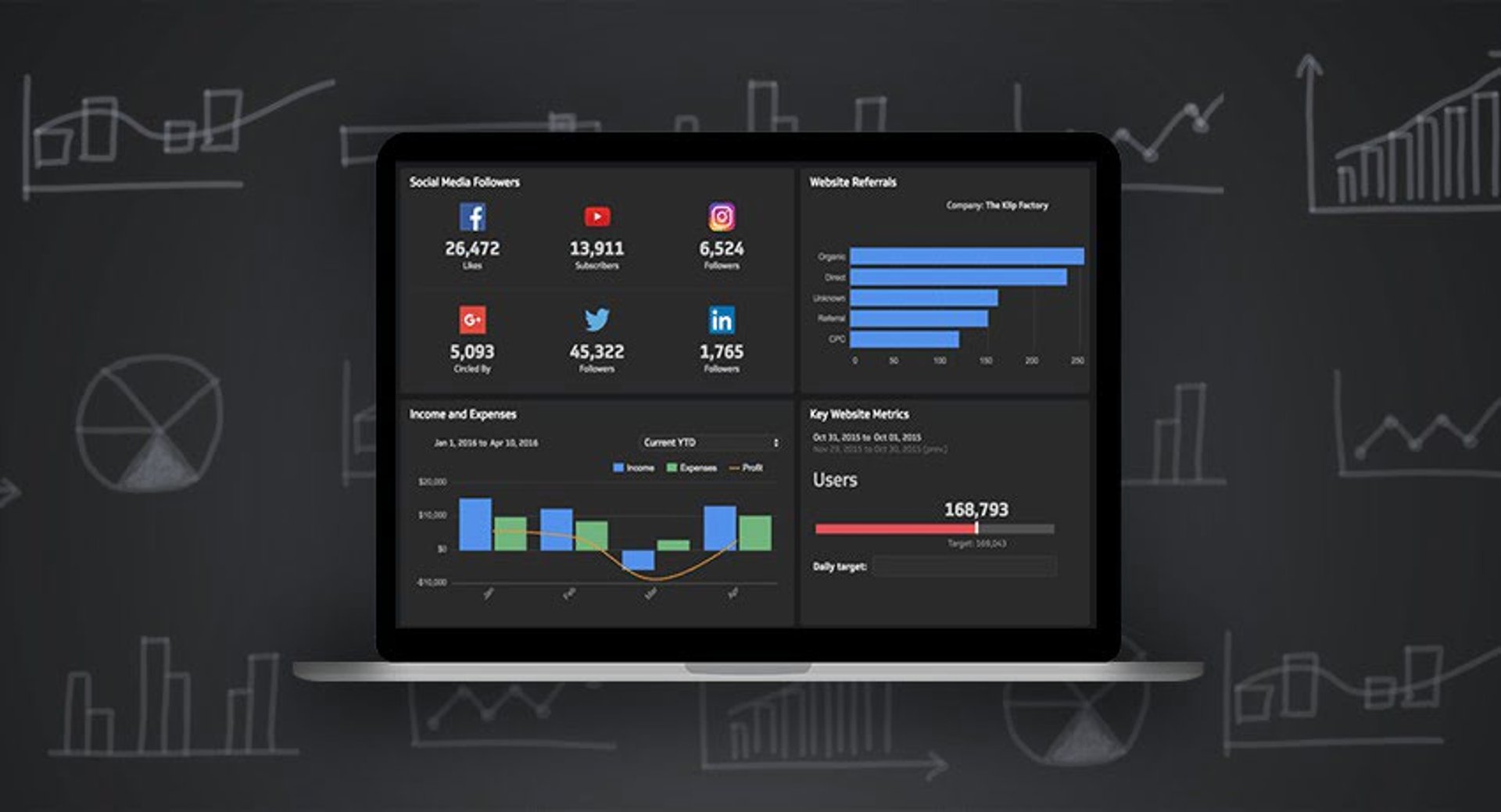
KPIs, metrics, and measures are the building blocks for how business performance is assessed and improved, so it’s important to understand the differences. It’s also key to know how to define your organization’s KPIs. Take it a step further and put your metrics and KPIs on a Klipfolio Klips dashboard so your entire organization can see performance.

What is a key performance indicator (KPI)?
The definition of a Key Performance Indicator (KPI) is a measurable value that shows how well a company achieves key business objectives.
Organizations use KPIs to measure progress toward targets. KPIs can be applied to industries, departments, or individual tasks. KPIs are evaluated over a set period and compared against past performance metrics or acceptable norms.
For example, a company could set a KPI to increase revenue by $10,000 this month. The KPI has a measurable value (dollar amount) and a specific time period (30 days). If it’s the 25th day of the month and revenue has increased by $15,000, it’s a clear sign the objective has been achieved.
Why are KPIs important?
KPIs are important because establishing, tracking, and reporting on your key performance indicators gives you a clear view of performance. KPIs provide values to compare against current results so you can see if and how you’re reaching goals.
With KPIs in place, you can set goals, develop tactics to reach them, evaluate results using business metrics, and keep a historical record of performance.
What is an example of a KPI?
Imagine you’re a small business owner who sells hand-crafted candles through an online store. You want to increase sales this quarter, so you set a KPI to sell 150 candles in the next 3 months.
You ask a few questions to define the KPI:
- What’s the desired outcome? Sell 150 candles in the next 3 months.
- How will you measure progress? Revenue measured in dollars.
- How can you influence the outcome? Run Google ads and improve on-site search performance.
- How often will you evaluate performance? Weekly.
- How will you know you’ve achieved the KPI? 150+ candles sold.
Now that the KPI is defined (sell 150 candles) and you know how to measure progress (revenue), decide which metrics to track to reach that KPI.

What is a metric?
A metric is a quantifiable measure used to track, compare, and assess performance or processes.
What’s the difference between a metric and a measure?
A measure is a fundamental or unit-specific number that can be summed, counted, or averaged.
A metric is derived from one or more measures and has a goal or performance context.
This difference is clearer when metric becomes “business metric,” meaning a quantifiable measure used to track and assess the status of a specific business process.
Why are metrics important?
Metrics measure business processes. They’re standardized and clearly named, so you can compare them across teams and time periods.
Metrics are measurements of a specific process, like the traffic volume on the website you built. A KPI might focus on a subset of that traffic, like the number of content downloads.
Key performance indicators drill into a key area, while metrics help you measure overall performance.
What is an example of a metric?
Back to the candle example. The overall business goal is to sell candles and make money. The KPI is to sell 150 candles in the next 3 months through the online store to reach a revenue target.
With that end goal in mind, here are useful metrics to track:
- Revenue: This metric measures the money you generate. If the goal is 150 candles at $15 each and you’ve sold $600 of product, you’ve sold 40 candles and still have 110 to go.
- Conversion Rate: How likely is a sale when a user visits the ecommerce store? This metric is total sales divided by total visitors over a period. If you’ve sold 40 candles over two weeks and had 200 visitors, conversion rate is 40/200 = 20%.
- Cart Abandonment Rate: The percentage of shoppers who add an item to their cart but don’t complete checkout. This helps you estimate potential revenue lost.
Revenue correlates directly to the KPI, while conversion and abandonment rates help flag issues and improvement opportunities.
Are KPIs and metrics the same?
No. KPIs and metrics work together. Key performance indicators are the end goals. Metrics are what you track along the way to determine if the goal will be met.

What is a measure?
In a data context, measures are numbers or values that can be summed or averaged, such as sales, leads, distances, durations, temperatures, and weight. The term is often paired with dimensions, which are categorical buckets you can segment, filter, or group, such as sales rep, city, product, colour, and distribution channel.
If your store sells candles and matches and you’ve sold 40 candles and 20 packs of matches, the units sold (40 + 20 = 60) is the measure and the dimension is the product type (candles or matches).
What’s the difference between a metric and a measure?
A measure is a simple number, like how many candles you’ve sold. A metric puts that measure into context. For example, what’s the average sale over the last 12 months?
Your metric could be Average Basket Size. It’s made of measures such as a) the number of transactions and b) the number of candles per transaction.
Why are measures important?
Both metrics and KPIs rely on and are derived from measures. Without measures you don’t have the building blocks to create a metric or define a KPI.
What is an example of a measure?
For an e-commerce business, Average Order Value is an important metric: it tells you the average amount of money spent on an order over a set period. The measures behind this metric are revenue (sum) and the number of orders placed (count). Divide revenue by orders to get average order value for a specific time period.
Now you’ve got the definitions, examples, and how they connect. Use them together on your dashboard to set targets, track progress, and improve results.
I hope this served as a good primer on what KPIs, metrics, and measures are, and that you now know the key differences between them.
Related Articles
Business Metrics vs. KPIs: What’s the Difference?
By Jonathan Taylor — March 13th, 2026
The 5 most important SEO KPIs for digital marketing success
By Sanket Patel — February 24th, 2026
Anatomy of a great API
By Danielle Hodgson — January 21st, 2026